Substation Automation
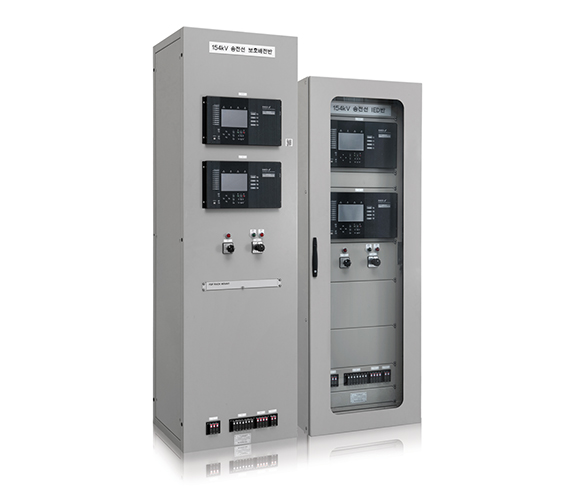
Transmission line Protection Panel
Transmission line Protection Panel

Transmission lines are one of the electrical power grid facilities used for electricity transmission from the generators to the consumers.
Transmission lines typically connect between substations. Since the length of transmission lines spans dozens of kilometers
by nature, transmission lines are exposed to natural environment and thus vulnerable to fault due to natural factors such as rain, wind
and lightening. Thus, the faultsoccur on the transmission lines more frequently than on the other types of facilities.
A reliable transmission line protection scheme is necessary because transmission lines not only deliver electricity but also
have great impacts on stability of electrical power systems due to changes in power flows when they get fault.
An IED is applied as a reliable main protection relay with a protection function that is designed to protect the target transmission
line section, and a separate IED is applied for backup protection having another protection function to widely protect the series of
transmission lines.
Transmission line Protection Panel
- An 154kV transmission line protection panel has a primary protection IED with PCM communication based current differential protection method (87L) and a secondary protection IED having 3-staged distance based protection method (21G, 21S). In addition, high-speed reclosing function (79) is activated in the primary protection IED.
Short-distance transmission line Protection Panel
- Transmission lines in urban areas are installed underground by their nature. Thus, their length should
be short. Since impedance-based distance protection scheme is not able to provide enough reliability
for short distance transmission lines, the secondary protection for such short distance transmission
lines tends to adapt both distance protection and the current differential protection.
In summary, an 154kV short distance transmission line protection panel applies PCM communication based current differential protection method (87L) as primary protection and combination of 87L and 3-staged distance method (21G, 21S) as secondary protection. Like the case of 154kV transmission line protection panel, high-speed reclosing function (79) is activated in the primary protection IED.
Transmission line Protection Panel
- Primary and secondary protection functions in 345kV transmission line protection panels are basically the same as the ones in 154kV transmission line protection panels. However, taking into account of the characteristics of circuit breakers that are able to trip by phases, the IEDs provide single-phase trip or 3-phase trip function depending on the type of faults. Since 345kV transmission line have a priority over 154kV transmission line, two identical panels are installed redundantly to provide reliability in protection. Like the case in 154kV transmission line protection panels, high-speed reclosing functions (79) are individually embedded in each of two primary protection IEDs with one of them activated according to the operation condition of the substation.
Specification
| Division | Item | Specification | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLP-K120 | SLP-K140 | SLP-K310 | ||
| Ratings | Input power | DC 90~140[V],60Hz | DC 90~140[V],60Hz | DC 90~140[V],60Hz |
| Rated voltage(PT) | 110/√3[V] | 110/√3[V] | 115/√3[V] | |
| Rated current(CT) | 5[A] | 5[A] | 5[A] | |
| Digital output | 10[A] : 250VAC 24 points |
10[A] : 250VAC 32 points |
10[A] : 250VAC 48 points |
|
| Digital input | DC 70 ~ 150[V] 40 points |
DC 70 ~ 150[V] 36 points |
DC 70 ~ 150[V] 24 points |
|
| Communication | Communication port | USB B-Type, Ethernet, Fiber Optic | RS-232, Ethernet, Fiber Optic | RS-232, Ethernet, Fiber Optic |
| Protocol | IEC61850, TCP/IP, IEEE C37.94 | IEC61850, TCP/IP, IEEE C37.94 | TCP/IP, IEEE C37.94 | |
| Time sync. | IRIG-B, SNTP | IRIG-B, SNTP | IRIG-B, SNTP | |
Main functions

- Main functions of differential current protection IED (SLP-Kxxx-87)
- Phase-segregated current differential protection (87L)
- Highly sensitive zero-sequence current differential protection for high-impedance ground faults (87G)
- Undervoltage and overcurrent based fault detection (UV/UVS/UVD, OC/OCD/OCG, OVG)
- High-speed one time auto-reclosing (79) (SLP-K310: single and 3-phase trip and reclosing)
- Transmission of trip information to opposite end to prevent single-end tripping
- Direct transfer trip (DTT) for circuit breaker failures (SLP-K310)
- Compensation for line charging current
- STUB and SOTF protection trip (SLP-K310)
- Out-of-step protection trip (SLP-K310)
- CT and PT failure detection
- External fault detection to prevent wrong tripping due to CT saturation
- Automated compensation for different CT ratios at both transmission line ends
- High-speed long-distance peer-to-peer communication between two IEDs based on IEEE C37.94 protocol
- Redundant communication lines for improved communication reliability
- Fully IEC 61850 compliant, Edition 1

- Main functions of distance protection IED (SLP-Kxxx-21)
- 3-staged (zone) distance protection (21) based on quadrilateral characteristics (SLP-K310: zone 4 applied for detecting faults on the overhead or underground portion of the line)
- Overcurrent based fault detection (OC/OCD/OCG)
- Undervoltage based fault detection (UV/UVS/UVD) (SLP-K310)
- Zero-sequence current compensation for zone 1&2 and zone 3 respectively
- Prevention of wrong tripping due to heavy load or overreach
- Power swing detection and zone 1/2/3 trip blocking
- Out-of-step protection trip (SLP-K310)
- STUB and SOTF protection trip (SLP-K310)
- Open line fault detection by detecting negative-sequence current and zero-sequence voltage
- PT failure detection, CT failure detection (SLP-K310)
- Fully IEC 61850 compliant, Edition 1


 CEO : LEE DONG RYUL
CEO : LEE DONG RYUL